Medium and thick plates are widely used in various fields as stress parts, such as bulldozers, excavators, loaders, railway passenger cars, and other construction machinery and locomotives. Medium and heavy plates usually refer to metal plates with a thickness between 4.5 and 25mm. The forming methods of medium and heavy plates mainly include: press brake bending forming, rolling machine forming, and press tolling forming. Bending(folding ) is a widely used and abundant product line forming method for the medium and thick plates.
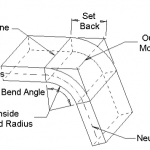
The difficulties of plate bending are long workpieces, high pressure, difficult forming, low efficiency, and difficult to control precision. The final result of bending is a comprehensive reflection of material parameters, process parameters, and mold parameters. Reasonable design of these parameters is the key to improving the bending performance of medium and thick plates.
The tonnage of press brake (press brake bending machine )
The first problem facing medium and thick plate bending is the tonnage selection of the press brake bending machine, and whether the bearing capacity of the fixture and the mold meets the requirements.
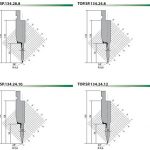
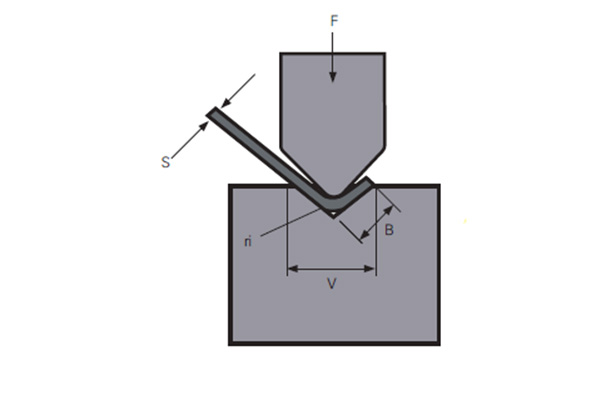
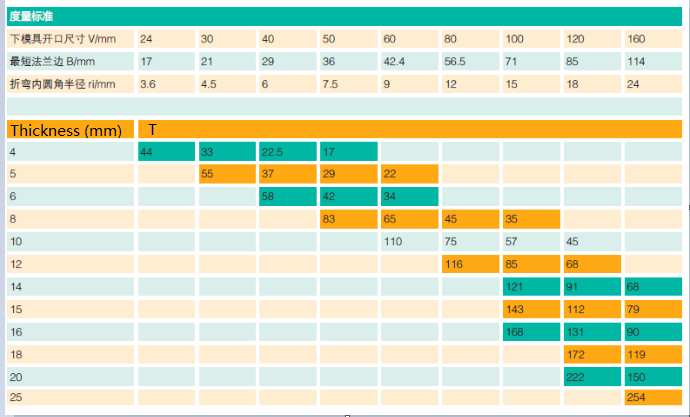
The force F is applied by the press brake bending machine to drive the mutual movement between the upper and lower molds, thereby bending the plate. For bending 90° carbon steel plates, WILA gives the empirical value of the plate stress load, as shown in Table 1. When the thickness of the carbon steel is 20mm, the lower die with V=160mm can be selected. At this time, the force load of the bending machine is 150t/m.
F=force per unit length (t/m);
S= material thickness (mm);
ri= bending radius of inner corner (mm);
V= lower die opening size (mm);
B= shortest flange edge (mm) );
aluminum: F×50%;
aluminum alloy: F×100%;
stainless steel: F×150%;
stamping and bending: F×(3~5)
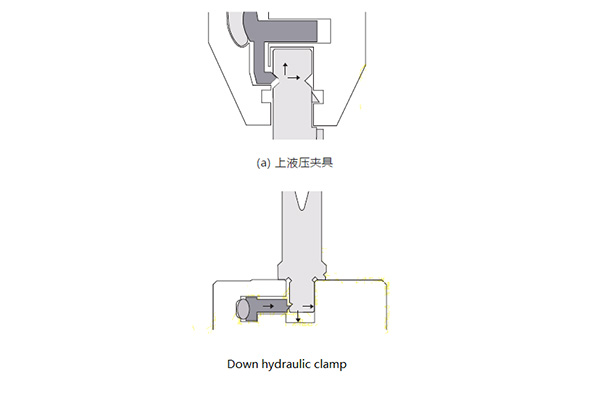
Heavy hydraulic clamp
The load-bearing methods of WILA heavy-duty upper hydraulic clamps include top load and shoulder load, and the maximum load is 250t/m and 800t/m respectively. The force-bearing surface of the fixture adopts CNC deep quenching hardening technology. The Rockwell hardness is 56~60HRC, and the hardening depth is up to 4mm, which has high hardness and strong wear resistance. The hydraulic clamp uses hydraulic rapid clamping, and the expansion of the hydraulic hose drives the movement of the clamping pin so that the mold is automatically seated and the bending line is automatically centered. For a bending mold with a total length of 6 meters, it only takes about 5 seconds for the hydraulic clamping to be fully clamped, and the comprehensive use efficiency is 3~6 times higher than that of the ordinary manual clamping system.
Heavy machinery compensation workbench
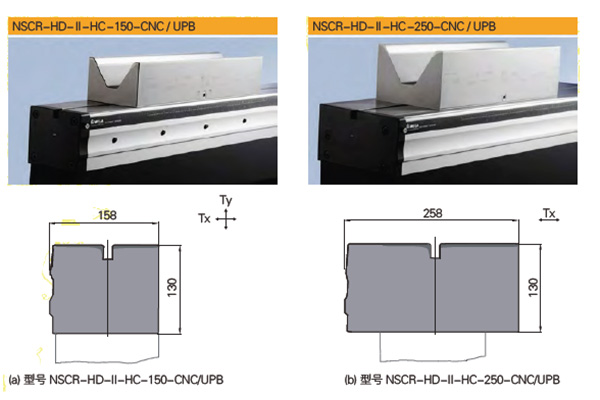
For the bending of medium and thick plates, WILA's new-level version of the heavy-duty mechanical compensation table can not only easily meet the load requirements, but also compensate for the deflection and deformation of the bending machine. The mechanical compensation workbench adopts hydraulic clamping, the surface accuracy can reach ±0.01mm, the rockwell hardness is 56~60HRC, and the hardening depth is up to 4mm. The mechanical compensation workbench adopts the universal UPB installation interface of WILA, which is easy to install and has higher accuracy. It also has its own Tx and Ty direction adjustments, which can ensure that the workbench and the backgauge remain parallel in the front and rear directions, and can perform local angular deviation correction.
Heavy bending die/tooling
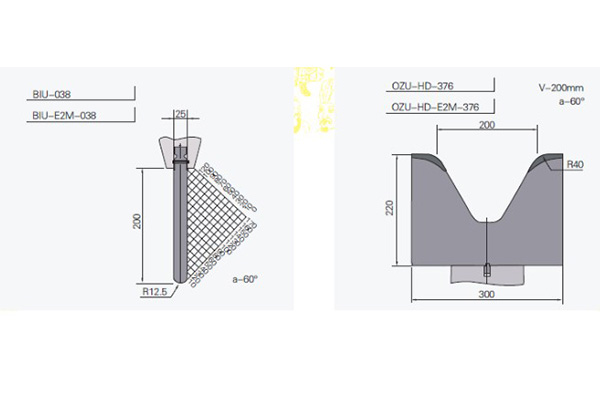
Due to the thickness of the plate, the lower mold with larger opening size (V24~V300) and the mold with larger bearing capacity are generally selected for the bending of medium and thick plates. The overall dimensions of the mold are generally large, and the weight of the mold has exceeded the normal handling capacity of the operator. With the help of roller bearings, WILA's patented technology E2M (Easy to Move) allows operators to move heavy bending molds conveniently, safely, and quickly, greatly saving mold replacement and machine adjustment time.
Bending molds with various knife shapes and lower mold openings that meet customer needs can be provided, such as straight knives, gooseneck scimitars, fillet molds, and multi-V molds. Through precise grinding of key parts, the dimensional accuracy of the mold is as high as ±0.01mm. Through the processing of CNC deep quenching and hardening technology, the mold hardness can reach 56~60HRC, and the depth of the hardened layer can reach 4mm.
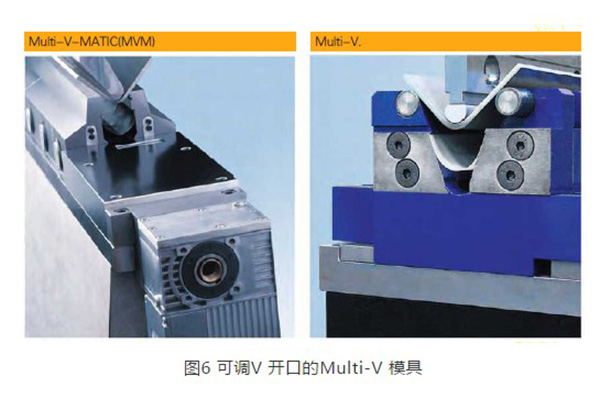
For the bending of medium and thick plates with different plate thicknesses, WILA also provides Multi-V molds, which are available in two forms: automatic adjustable V port and manual adjustable V port, as shown in Figure 6. Through the numerical control motor or the adjustment block, the V opening size of the lower mold can be adjusted arbitrarily according to the characteristics of the plate, which is especially suitable for bending medium and thick plates with high rebound and high strength. At the same time, the Multi-V mold comes with hardened rollers with a low friction coefficient, which can greatly reduce the external creases of the bending parts, and at the same time, it can reduce bending by 10%~30% compared with the traditional lower mold.